The European Nitrates Directive, the Groundwater Directive and the German Groundwater and Drinking Water Ordinances require that exceedances of the limit value for nitrate of 50 milligrams per liter be prevented.Since 2008, the quality standard has been exceeded every year at almost one in six measuring points.Extensive changes to the fertilizer legislation have allowed the designation of particul... read more
nitrogen
Umwelt-Indikator
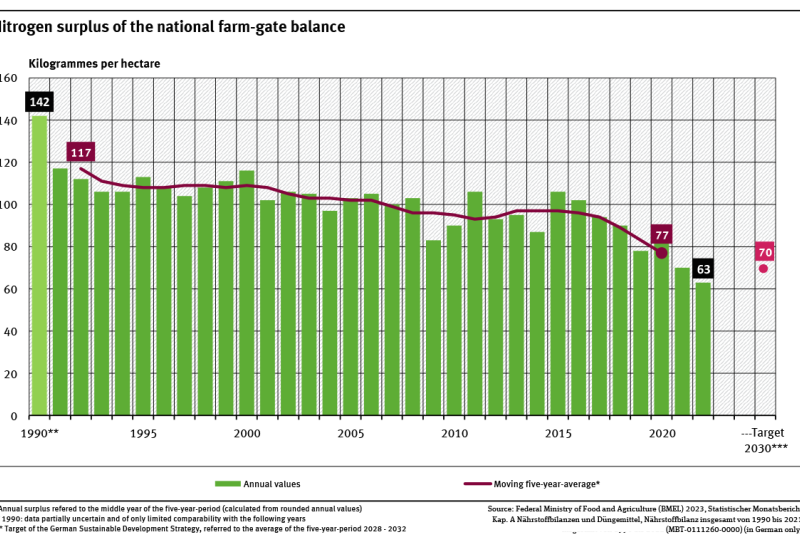
Indicator: Agricultural nitrogen surplus
The five-year average of nitrogen surplus of the total balance per hectare of utilized agricultural land has decreased by 34 % since 1992.The Federal Government aims to reduce the average nitrogen surplus of the total balance of the years 2028 to 2032 to 70 kilogrammes per hectare of agricultural land.If the trend of the last 10 years continues, the target will be reached. read more
Indicator: Nitrogen eutrophication
69 % of vulnerable ecosystems in Germany are threatened 2019 by excess nitrogen deposition.With the revised German Sustainable Development Strategy 2016, the Federal Government aims to reduce the proportion of these areas by 35 % until 2030. According to the current calculation basis, this results in a target value of 52 % by 2030.This target is feasible only if efforts to reduce air pollution are... read more
Air
Reactive nitrogen
Reactive nitrogen, unlike nonreactive molecular nitrogen (N2), is in a great many organic and inorganic substance compounds and of vital importance to all life processes. The availability of reactive nitrogen often limits plant growth, which is why sufficient supply of reactive nitrogen is so important in food production. If excessive amounts of reactive nitrogen are deposited to the environment,... read more
News on Agriculture
8th Global Nitrogen Conference
The 8th Global Nitrogen Conference of the International Nitrogen Initiative (INI 2020) follows up on the previous nitrogen conferences that have been held since 1998. This year’s theme is “Nitrogen and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”. Most of the SDGs are closely related to the nitrogen cycle. read more
News on Soil | Land
Environment and agriculture – Overview for Germany
More than half of Germany's surface area is used for agriculture. Agriculture thus is the largest land user in Germany and a significant contributor to environmental stress. On the other hand, agriculture is also affected, for example, by the effects of climate change. In the flyer "Environment and agriculture 2018" UBA presents key facts about agriculture and environment. read more
Agriculture
Nitrogen
In as much as nitrogen is an indispensable nutrient for all living things, the use of mineral and organic nitrogen fertilizers to increase crop yields is a common practice. It is essential that such fertilizer be used judiciously and on a needs oriented basis. Nitrogen surpluses can damage terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and can have harmful climatic, air quality, and biodiversity effects. read more